Peptic means stomach related Ulcer means sore or break-in. Peptic ulcer or Peptic ulcer disease is an extremely painful ulcer or sore formation in the mucosal layer of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Ulcers develop as a result of an imbalance between aggressive factors and defensive factors of the stomach. It is generally present in the oesophagus or other parts of the stomach or proximal duodenum in the small intestine and is referred to as oesophagal ulcer, Gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer respectively. Ulcers can also form in the distal duodenum, or the jejunum (Ramakrishnan and Salinas, 2007).
Risk factors:
Ulcers usually occur as a result of an imbalance between pepsin and gastric acid secretion. The most common causative factors of ulcers include Helicobacter pylori infection, excessive use of NSAIDs, increased acid secretion driven by stress, spicy food, consumption of caffeine, alcohol or smoking. Peptic Ulcers can lead to many issues like perforation, GI bleeding, and blockage if left untreated. (Lee et al., 2017)
TYPES OF PEPTIC ULCERS
There are three different kinds of the peptic ulcer which are as follow:
- Gastric ulcers
- Duodenal ulcers
- Oesophageal ulcers
These types of ulcers are most commonly caused either by infections with Helicobacter pylori bacteria or by chronic use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. (Staff, 2020)
Gastric ulcers
Stomach ulcers are also known as Gastric ulcers, are sores on the mucosal membrane of the stomach.
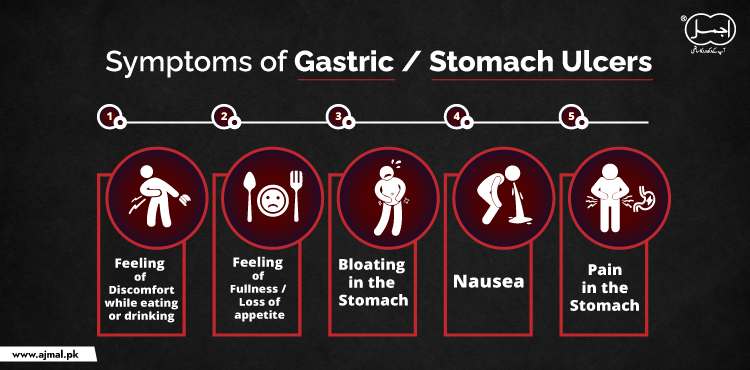
Symptoms of gastric/stomach ulcers
- Feeling of discomfort while eating or drinking.
- Pain in the stomach.
- Feeling of fullness/ loss of appetite.
- Bloating in the stomach.
- The discomfort remains for a number of minutes or hours.
Modern Treatment
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) work by bringing down the quantity of acid in your stomach avoiding further damage to the ulcer. Examples of PPIs are omeprazole, pantoprazole and lansoprazole. (Staff, 2020)
Duodenal ulcers
A duodenal ulcer is a type of peptic ulcer that is formed in the first part of the small intestine.
Symptoms of duodenal ulcers
- Pain and discomfort in the abdomen.
- Difficulty indigestion.
- Nauseous feeling.
- Weight reduction.
Modern Treatment:
Week course of acid suppressants will relieve ulcers.
Oesophageal ulcers
An oesophagal ulcer is an open sore that forms in the mucous lining of esophagus or at the spot where esophagus links to the stomach.
Symptom
- Difficulty in swallowing.
- Nau
- Acid rebound.
- Dry cough.
Modern Treatment
Usage of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) will relieve these kinds of ulcers as well. Examples include Omeprazole’, rabeprazole etc (Elaine Gottschall).
Pathophysiology
The integrity of the gastric lining of upper GIT depends upon the balance between “aggressive/triggering’’ factors (e.g, gastric acid, H. pylori, NSAIDs and pepsin), and “defensive/protective” factors (e.g, prostaglandins, mucus, bicarbonate, and blood flow to mucosa). Peptic ulcer disease is produced by an imbalance between aggressive factors and defensive factors I.e, Excessive gastric acid secretion and decreased defence mechanism (Yuan et al., 2006).
Inhibition of endogenous prostaglandin synthesis causes a decrease in epithelial mucus, mucosal blood flow, bicarbonate secretion, epithelial proliferation, and mucosal resistance to injury. Decreased mucosal resistance increases the incidence of injury by endogenous and exogenous aggressive factors such as acid, pepsin, bile salts, NSAIDs, ethanol and other noxious agents (Yuan et al., 2006).
Diagnosis of peptic ulcer
To diagnose an ulcer and its cause the doctor uses details from the medical history of the patient, a physical exam, and tests. The existence of an ulcer can only be decided by looking directly at the stomach with an endoscopy or an X-ray test.
Lab tests
To check, if your patient has a Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, most physicians rely on these tests:
Blood test
Endoscopy and Biopsy of Upper Gastrointestinal (GI)
In the endoscopy of an upper GI, a gastroenterologist, surgeon, or other trained health care personnel uses an endoscope to see inside the upper GI tract. A hospital or an outpatient centre is used to perform this procedure.
An intravenous (IV) needle is placed in the patient’s arm to inject a sedative. Sedatives assist a patient stay relaxed and comfortable during the process. In some cases, the action can be performed without sedation. The patient can also be given a liquid anaesthetic to gargle or spray an anaesthetic on the back of the throat. The doctor carefully inserts the endoscope down the esophagus and inside the stomach and duodenum. A small camera supported on the endoscope sends a video image to a monitor, allowing close testing of the lining of the upper GI tract. The endoscope pumps air into the stomach and duodenum, making them uncomplicated to see.
The doctor may carry out a biopsy with the endoscope by taking a small piece of tissue from the lining of the esophagus. You won’t feel the biopsy. A pathologist looks over the sample in a lab.
Upper GI series
An upper GI series looks at the shape of the upper GI tract. An x-ray technician carry out this test at a hospital or an outpatient centre. A radiologist reads and reports on the x-ray images. This process does not require anaesthesia. A health care professional will tell how to get ready for the procedure, which involves when to stop eating and drinking.
In the course of the procedure, the patient will stand or sit in front of an x-ray machine and drink barium, a chalky liquid. Barium coats the mucosal lining of esophagus, stomach, and small intestine so the doctor can observe the shapes of these organs more distinctly on x-rays.
The patient may have bloating and nausea for a short duration after the test. For several days afterwards, the patient may have white or light-coloured excreta from the barium. A health care professional will direct all about eating and drinking after the test.
Computerized tomography (CT) scan
A CT scan uses a combination of x-rays and computer technology to generate images. For a CT scan, a health care professional may give the patient a solution to drink and an injection of a special dye, which doctors call a contrast medium. The patient will lie on a table that slides into a tunnel-shaped appliance that takes the x-rays. An x-ray technician performs the procedure in an outpatient centre or a hospital, and a radiologist explains the images. This process doesn’t require anaesthesia.
CT scans can help diagnose a peptic ulcer that has created a hole in the wall of the stomach or small intestine.
(NIDDK, 2014)
Mahiyat wa Asbab or Aetiopathogensis and Causes:
In Unani Medicine, the disease is caused by disturbance of equilibrium of akhlat arba factors viz. mizaj (temperament) tarkeeb (structure) and ittesal (continuity of tissues) which needs to be maintained the for a healthy life.
Any differences and abnormalities in akhlat arba are known as:
- Sue mizaj or change of
- sue tarkeeb or change of
- tafarruqe Ittesal or the discontinuity in tissues.
The alteration of mizaj causes a change in the balance of four kaifiyate arba/qualities i.e. hotness/haraarat, coldness/baroodat, mistress/ratoobat and dryness/yaboosat. So it is considered as sue mizaj sada and it will be considered as sue mizaj maddi if the imbalance is at the level of body fluids/humors (Akhlat) (Hafeel et al., 2018).
Etiology or Asbab:
A large number of the Unani scholars explained the following cause of gastric ulcers: Accumulation of matters like khilte balgham from the brain, bile from the liver or black bile from the spleen.
- khilt-e-haad (irritant and corrosive humours)
- Motaffin nawazil (purulent matter)
- Motaffin fuzlat (waste materials) in the stomach and get infected
- Consumption of Haar (hot), spicy (tez) and tursh (acid) food like vinegar (sirka) ultimately leads to the formation of pustules and ulcers in the stomach.
- As a result of gastritis (Waram e medi) (Hafeel et al., 2018).
Nishaniyan wa Alamat or Signs and Symptoms
In Unani medicines, physicians have described the signs and symptoms of Qarahe Medah in. This is quite similar to the description of Gastric ulcers by gastroenterologists in their modern scientific research. According to Unani literature Razi Jurjani Ibn Hubal Baghdadi ulcer patients possess the following typical signs and symptoms:
- Bad smell of mouth (Nakhush Boe Dahan).
- Bad-smelling belches(Badboodar Dekarain).
- Dryness of palate and tongue (Lesaan aur Talu ki Yabusat).
- Increased nausea and vomiting (Kasrate Qae wa Ghisyan).
- Appearance of ulcer debris and scabs in vomiting (Qishore ki Maujodgi).
- Low-grade fever (Khafif Hararat).
- Epigastric pain and irritation (Naaf ke ooper lez’a) worsens on the consumption of hot, spicy and acidic food. (Ahmed and Khan, 2018)
Elva / aloe
Itscientific Name: Aloe buettneri A. Berger
Family: Liliaceae
Actions: Mushily, mudir, muhallil (Ahmed and Khan, 2018)
Elva is frequently used to treat inflammation and gastric ulcer in Togolese folk medicine The Hydro-alcohol extract of Aloe possess anti-inflammatory, wound healing properties and anti-ulcer
(Metowogo et al., 2008).

Adrak / ginger
Scientific name: Zingiber officinale
Family: Zingiberaceae
Part used: Rhizome
Actions: possess Kasire riyah, Hazim, Jali, Munaffise balgham actions (Ahmed and Khan, 2018)
The indomethacin-induced ulcer can be prevented by the use of methanolic or ethanolic extract Z. officinale. Due to its high flavonoid and antioxidant content Ulcer patients are advised to consume ginger as much as possible. Using methanoic or ethanoic extract of Z. officinale in the prevention and treatment of indomethacin-induced ulcers and other types of ulcer induction can be further confirmed (Airaodion et al., 2019).

Papaya
Scientific Name: Carica papaya
Family: Caricaceae
Part used: Seed (Ahmed and Khan, 2018).
Carica papaya is an important fruit and its seeds are used in the treatment of ulcers in Nigeria. Aqueous extract of Carica papaya seed possesses anti-ulcerogenic and antioxidant properties against an indomethacin-induced peptic ulcer in male rats (Oloyede et al., 2015).
Unripe C. papaya extracts contain constituents like alkaloids, flavonoids, glycosides, terpenoids, carbohydrates, saponins, and steroids. The anti-ulcer property of the unripe fruit is a consequence of the cytoprotective and antimotility properties of the extracts (Ezike et al., 2009).

Asl-Us-Soos/ Liquorice
Scientific name: Glycyrrhiza glabra
Family: Fabaceae
Part used: Wood
Actions: Munzij, Muqawwie asab, Muhallil-e-warm, munaffise balgham, kasir-e-riyah (Ahmed and Khan, 2018)
A derivative of glycyrrhetinic acid Carbenoxolone which contains a steroid-like structure is present in the root of the liquorice plant. Carbenoxolone is effective in the treatment of gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers. Liquorice can increase the concentration of prostaglandins in the digestive system which ultimately leads to the promotion of mucus secretion from the stomach, it also increases the life span of surface cells in the stomach. Liquorice also has anti pepsin effects (Ishtiyaq et al., 2019).

Asgand
Scientific Name: Withania somnifera
Family:Solanaceae
Part used: Root
Actions: Muqawwi-e-aam, Muhallile warm, Musakkin-e-Asab, Munawwim, Muqawwie-meda, moalide mani (Ahmed and Khan, 2018).
Root extracts of Withania somnifera have significantly decreased the ulcers that are induced by the administration of ethanol in rats. when it is compared with standard drugs like Sucralfate and Alpha Lipoic Acid powder it shows gastroprotective and ulcer protective activity. This gastroprotective activity is attributed to the presence of flavonoids and antioxidants in the extract (Raghuveer et al., 2013).

Kalonji
Scientific name: Nigella sativa
Family: Ranunculaceae
Part used: Seed
Actions: Jali, Munaffise balgham, muqawwi-e-meda (Ahmed and Khan, 2018)
Nigella sativa possesses prostaglandin-mediated and/or through its antioxidant and anti-secretory activities and these activities are attributed to its antiulcer effects.

Khulanjan
Scientific Name: Alpinia galanja
Family: Zingiberaceae
Part used: Root
Actions: muffarrah, muqawwi-e-qalb meda wa Bah, muttaiyyaib-e-dahan, Munaffise balgham, Kasir-e-riyah, muhallil-e-warm (Ahmed and Khan, 2018).
From the wild seeds of Alpinia galanga potent anti-ulcer principles, like 1′-acetoxychavicol acetate (1) and 1′-acetoxyeugenol acetate (2), were isolated (Mitsui et al., 1976)erted through cyclooxygenase and . antiulcer effects are exnon-cyclooxygenase pathways by Alpinia officinarum extract and galangin. Hence, validating use of galangin as a treatment for gastric damage (Gong et al., 2018).

Kishneez
Scientific Name: Coriandrum sativum
Family: Apiaceae
Part Used: Fruit
Actions: Musakkin, muhall-e-warm, muqawwie qalb wa dimag wa meda, kasir riyah, Qabiz (Ahmed and Khan, 2018)

Turmeric/ Haldi
Scientific Name: Curcuma longa
Family: Zingiberaceae
Part Used: Rhizome
Actions: Muhalil-e-warm, musakkin, Jali, Mujaffif, Daf-e-Tashannu (Ahmed and Khan, 2018).
Curcuma longa has been used as a traditional remedy commonly for a variety of symptoms such as inflammation (waram), gastritis (waram-e-maida) and gastric ulcer (Qarhe Maida). When pylori-ligated rat stomachs were administered per os with C. longa extract, gastric acid secretion was reduced and it also protected against the formation of gastric mucosal lesions (Kim et al., 2005).

Gaozaban
Scientific name: Borago officinalis
Family: Boraginaceae
Part used: Flower, leaves
Actions: Mutadil Munaffise balgham, mulattif, muharriq, muqawwi-e-qalb (Ahmed and Khan, 2018).
It has been reported recently that Borago officinalis extracts may contain gastroprotective effect against indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers. The antioxidant properties of phenolic glycosides, flavonoids, and tannins which are present in the extracts may be responsible for these gastroprotective effects (Di Cerbo et al., 2020).